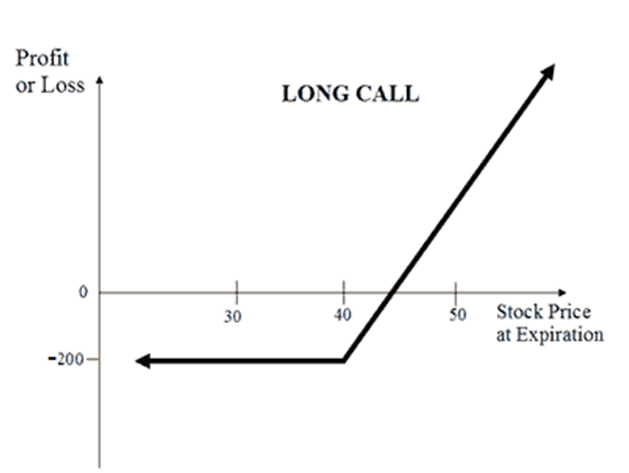
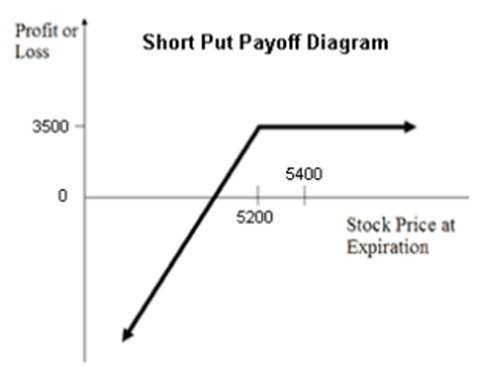
The obvious strategy to reveal that is exhibiting you a payoff profile (the doable path of your P&L for the commerce at completely different underlying costs):
Lengthy Name:
Brief Put:
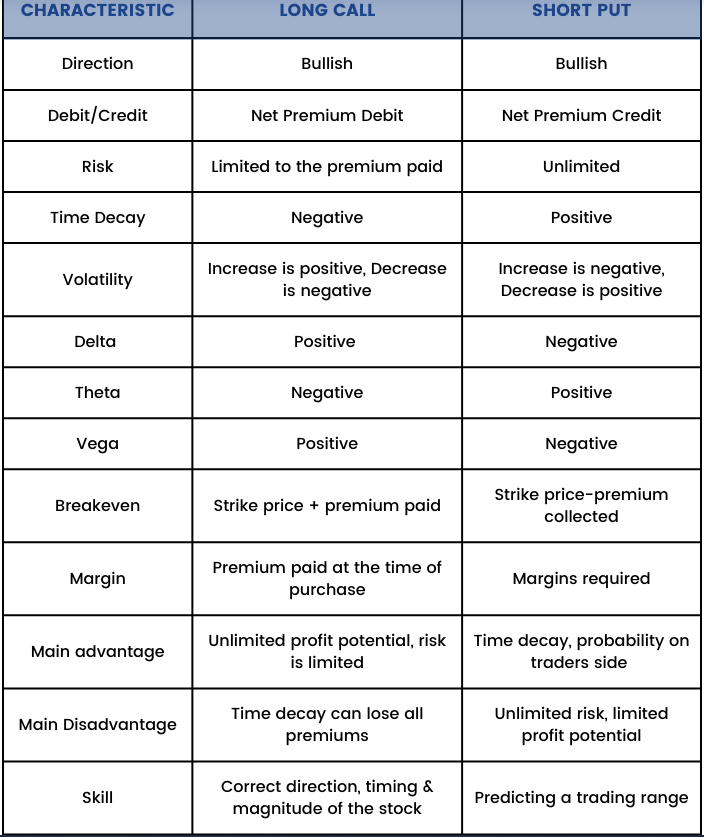
There are instant variations.
You purchase a protracted name once you suppose the market will go up rather a lot. You are optimistic and keen to danger some money within the hopes of creating a a number of of that.
You promote a put once you suppose the market will not go down rather a lot. You are assured that the market will not go down. By promoting a put to a different dealer, you are virtually performing as a bookie, taking a price to permit one other dealer to make an enormous wager. If he is mistaken, you get to maintain his wager. For him to be proper, the market has to maneuver sufficient to neutralize the money worth of his wager.
Motive #1: You Have Motive to Imagine the Market Will Go Up. A Lot.
In the event you’re bullish on a inventory, there’s a whole lot of issues you are able to do to specific that view.
● You should buy the inventory
● You should buy calls on the inventory
● You should buy the inventory and promote lined calls towards it
● You should buy the sector ETF or a basket of associated shares for a sympathy play
● You may promote places towards the inventory
● You may enter any variety of directionally bullish choices spreads
All bullish outlooks, however very completely different P&L paths.
Shopping for a protracted name makes probably the most sense.
Motive #2: Different Merchants Disagree With You (Low Volatility)
Skilled choices merchants are fond of claiming that anytime you commerce choices, you are betting on volatility, whether or not you plan to or not.
It is because choice costs are inherently tied to the anticipated future value motion of the underlying asset. In different phrases, shopping for choices is dear when individuals suppose the market will transfer rather a lot, and vice versa. Therefore, shopping for places or calls on a inventory like Tesla is rather more costly (as a share of the inventory value) than a extra tame inventory like Johnson & Johnson. Tesla makes wild value strikes on a regular basis, whereas Johnson & Johnson stays steady more often than not.
Within the choices world, this concept of the market’s expectations about future value fluctuations known as volatility. When choices merchants say a inventory is “high volatility,” they imply that merchants anticipate the inventory value to fluctuate rather a lot sooner or later and choices on that inventory are costly.
Think about Tesla is saying earnings tomorrow, within the first quarter after the Tesla Semi is on sale. If the outcomes are dangerous, the inventory will tank. If outcomes are good, it should skyrocket. All merchants know this and therefore shopping for places and calls is dear to account for the large transfer. There is not any free lunch.
However whereas Tesla’s baseline volatility is excessive in comparison with the typical inventory it has it is personal ebb and circulation cycle. Volatility is relative. You may’t say Johnson & Johnson’s volatility (i.e. choice costs) are low cost as a result of it is cheaper than shares like Tesla. Each of them are priced the way in which they’re for good motive.
As a substitute, volatility is relative to itself. So it’s best to examine Tesla’s volatility to the inventory’s personal historic volatility. Is volatility low cost, common, or costly right this moment in comparison with latest historical past?
A technique to do that is utilizing a measure like implied volatility rank, or IV Rank. It measures how costly a inventory’s choices are as a percentile in comparison with the previous 12 months.
Motive #1: To Capitalize on Costly Choice Costs
As we mentioned, each choice commerce is an implicit volatility. Shopping for an choice outright is taking the view that volatility (or the market’s estimate of how a lot the market will transfer till expiration) is underpriced, and vice versa.
In the event you spend time in skilled buying and selling circles, you will discover that profitable choice merchants are inclined to promote volatility way more typically than they purchase it. That is because of the “volatility risk premium.”
This concept of a volatility danger premium comes out of academia. Students have basically discovered that merchants that promote volatility when it is excessive are inclined to make extra returns. And there is a good motive for that. Excessive volatility signifies a excessive degree of market stress.
And when buyers are harassed, the very first thing they wish to do is defend what they’ve. Everybody doing this without delay pushes up the value of safety briefly till the market calms down.
When a inventory declines shortly, buyers will rush to purchase places they usually’ll develop into expensive–opening a chance to promote probably overpriced choices.
Nevertheless it’s not so simple as promoting costly choices. Promoting a put is a directionally bullish strategy–in different phrases, you want a compelling motive to be bullish on the underlying inventory.
Motive #2: You are Reasonably Bullish on a Inventory
There are occasions once you’re extra certain {that a} inventory will not fall than you might be that it’s going to rise.
There are many conditions like these.
A inventory caught in a long-term buying and selling vary with no evident catalysts.
Or maybe a stalwart inventory inside a bull market. Whereas Apple (AAPL) is not the very best flying inventory, it is uncommon to see its shares plummet in a steady bull market.
Some merchants will even promote places towards takeover targets, surmising that there is a “floor” to their inventory value because of the takeover curiosity.
Shopping for calls and enjoying for the house run is not the fitting transfer for shares like these. However you continue to have a market view you are assured in and wish to revenue from. Promoting a put permits you to generate earnings so long as the inventory does not decline rather a lot, which turns out to be useful in steady bull markets.